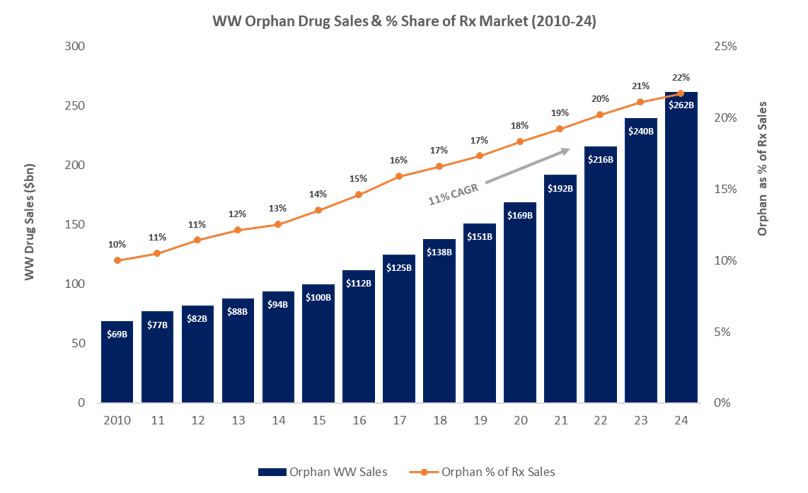
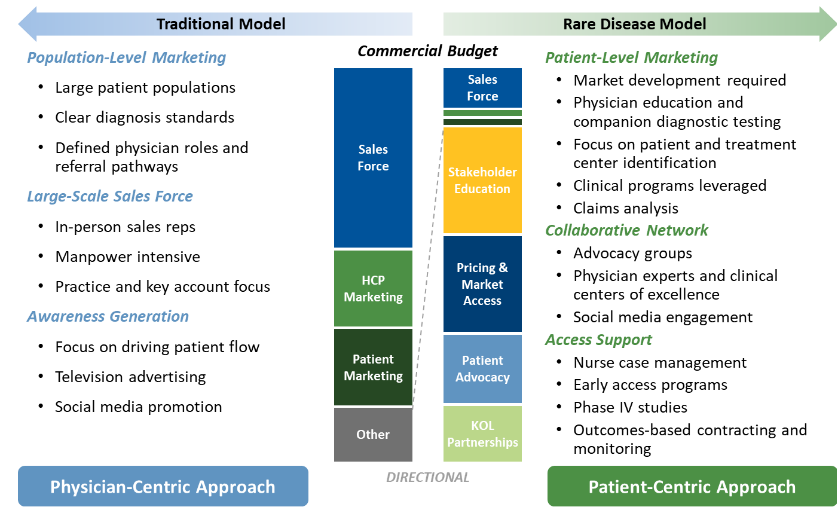
Why Your Orphan Drug Needs A Global Market Access Strategy
Key Takeaways
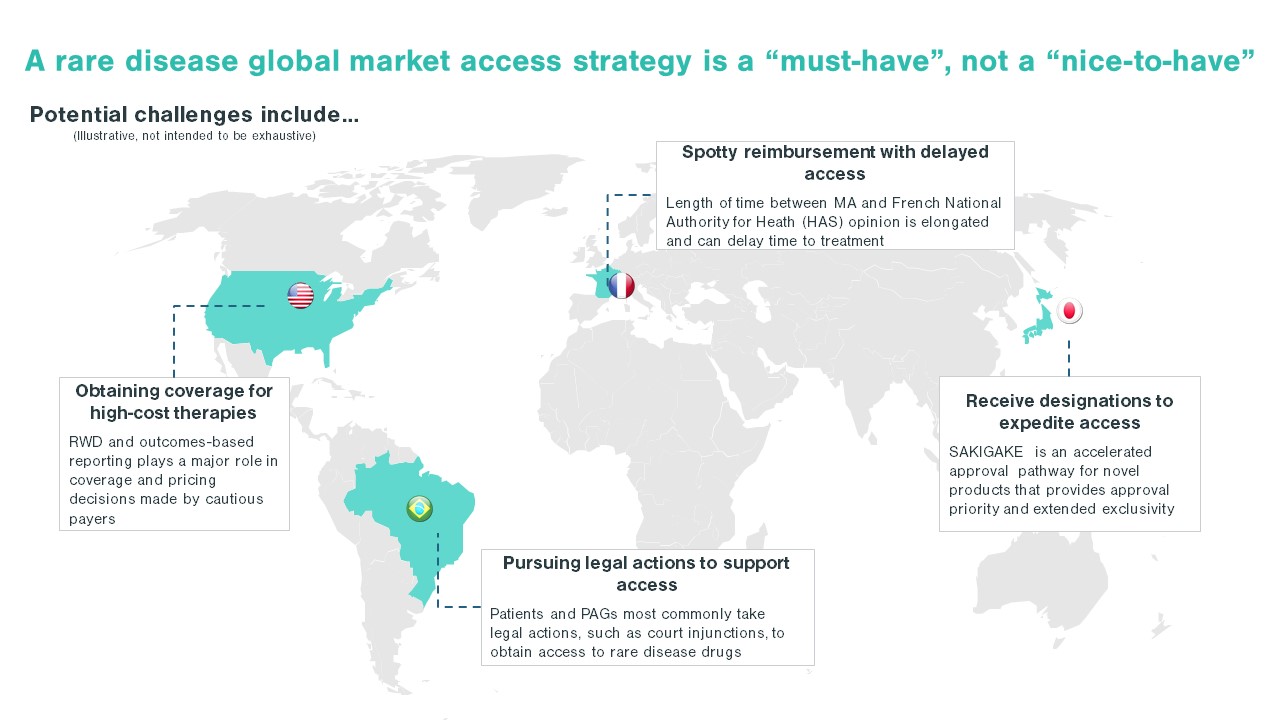
- An effective global market access strategy for rare diseases requires a higher degree of regional customization compared to other launch prep activities
- While regulatory approval in first-tier US and EU markets can often translate on a global scale, as many local regulatory bodies look to FDA or EMA approval as the gold standard, local market access requirements vary significantly
- This variation includes, among other factors:
- Price referencing
- Health technology assessments
- Public vs. private payer dynamics
- Rebates and discounts
- Reimbursement restrictions (e.g., step-through requirements)
- Real-world-evidence-based payment models
- Companies must be ready to develop individual market strategies to address these country-specific challenges
Why You Need A Global Market Access Strategy
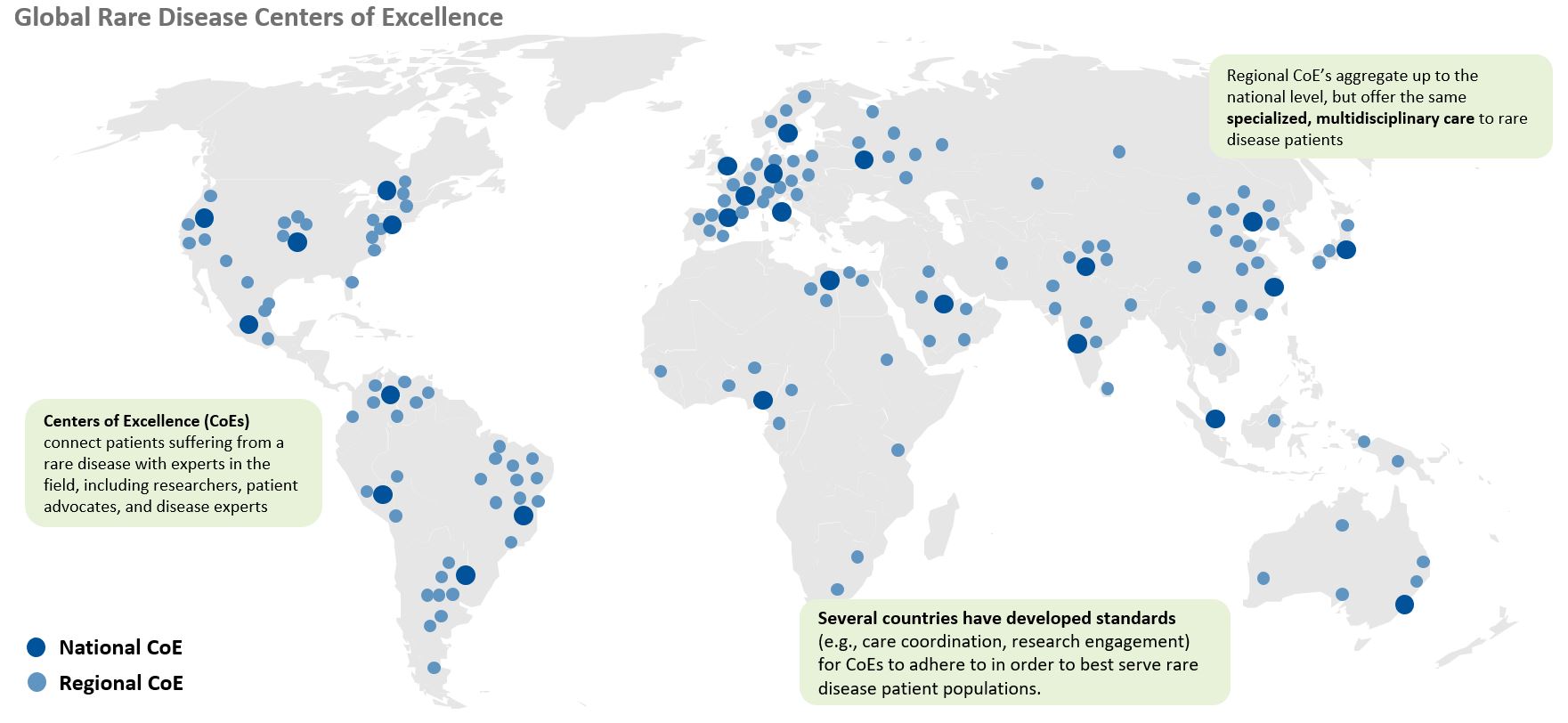
Each country poses unique challenges in developing a rare disease market access strategy. While some areas face a scattered patient population, others may face challenges such as immature physician and patient advocacy networks. Additionally, the high cost of certain drugs, like gene therapies, are handled differently by different countries. These nuances in market behaviors and structure underlie the importance of looking across the global landscape when developing a market access strategy. For US-based pharma companies, developing a comprehensive market access plan, rather than simply pivoting off a US-focused market access strategy, will ensure the long-term launch plan meets global needs and is positioned for success.
How To Develop A Global Market Strategy
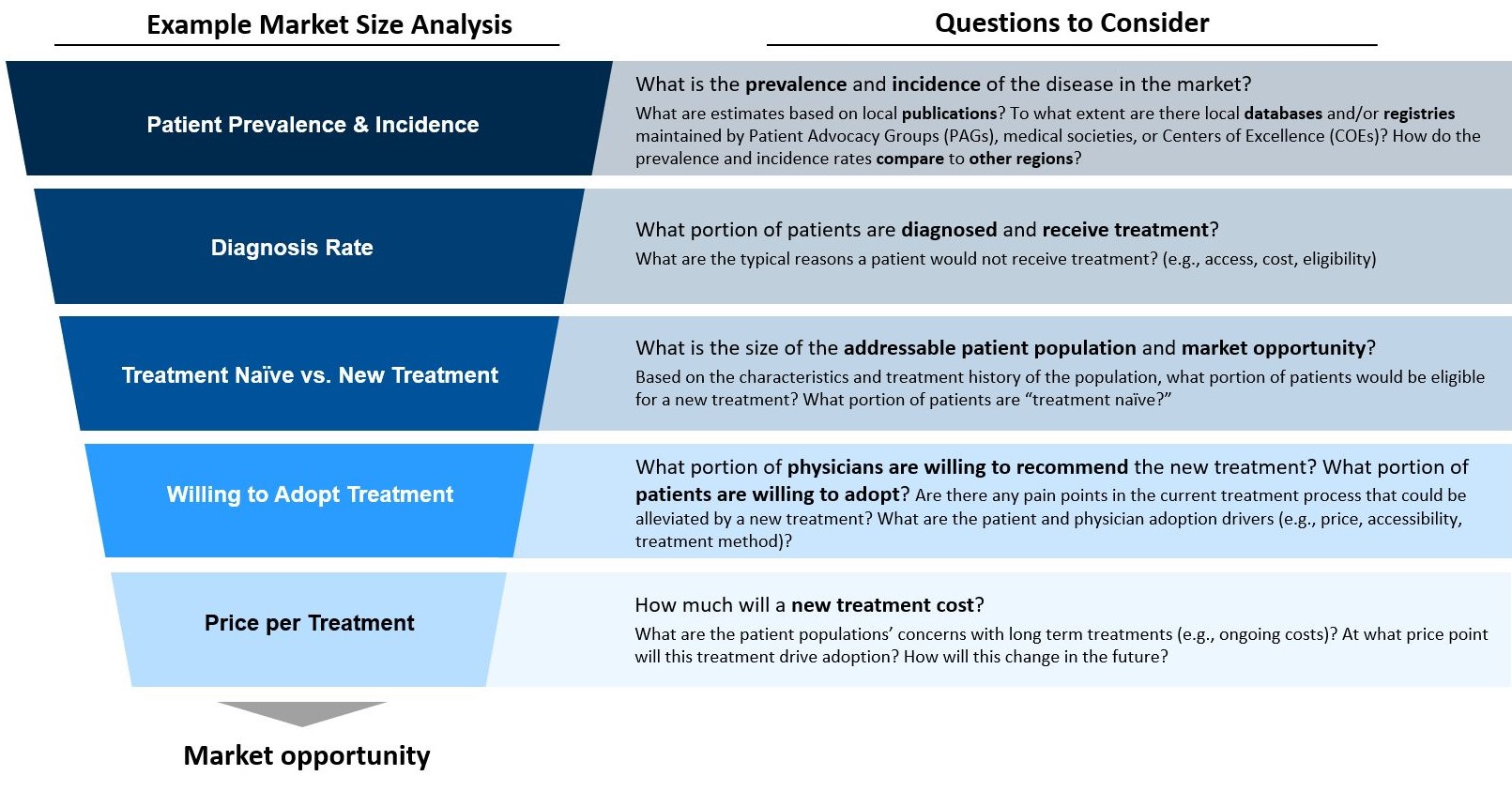
Rare disease companies need to answer complex key questions:
- Which markets will be targeted for launch?
- How much compromise in pricing is possible to gain access in global markets, particularly given reference pricing?
- What evidence is available or will be developed to support global market access?
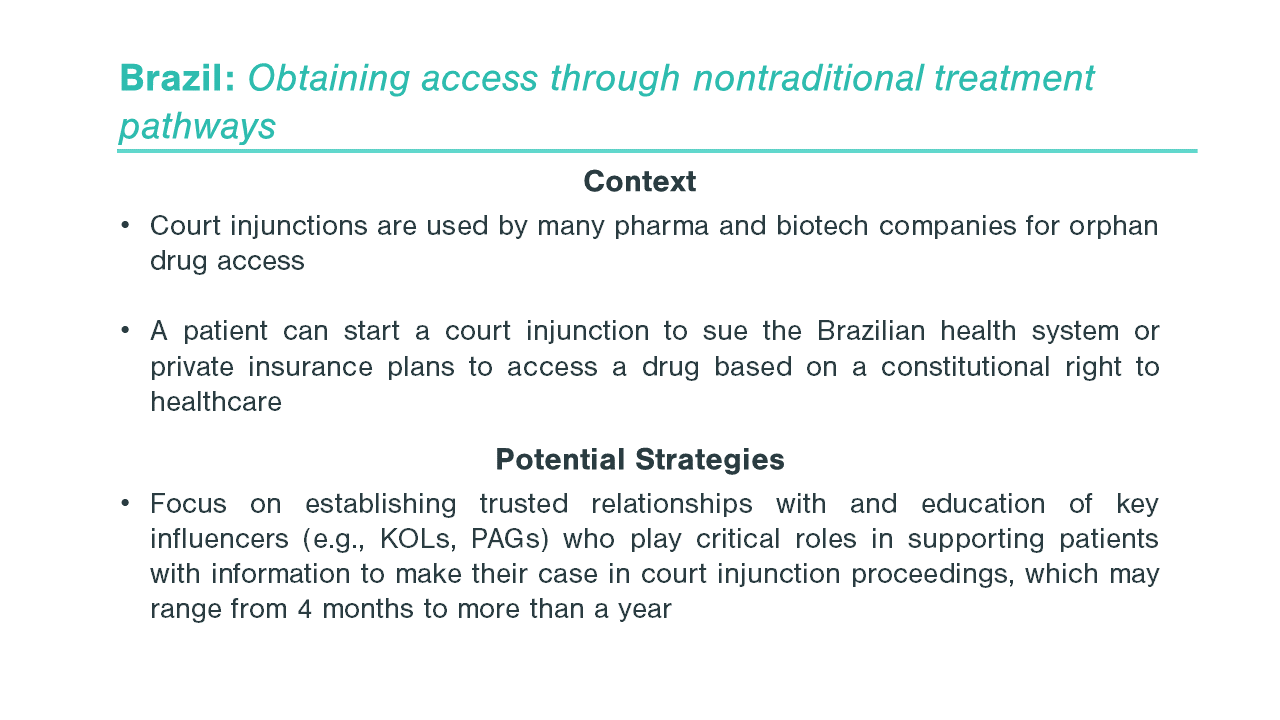
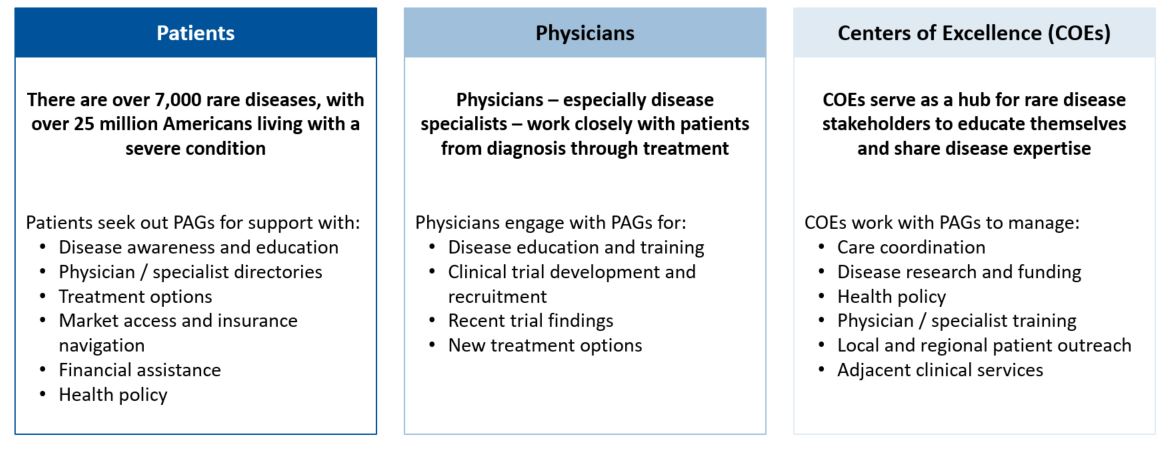
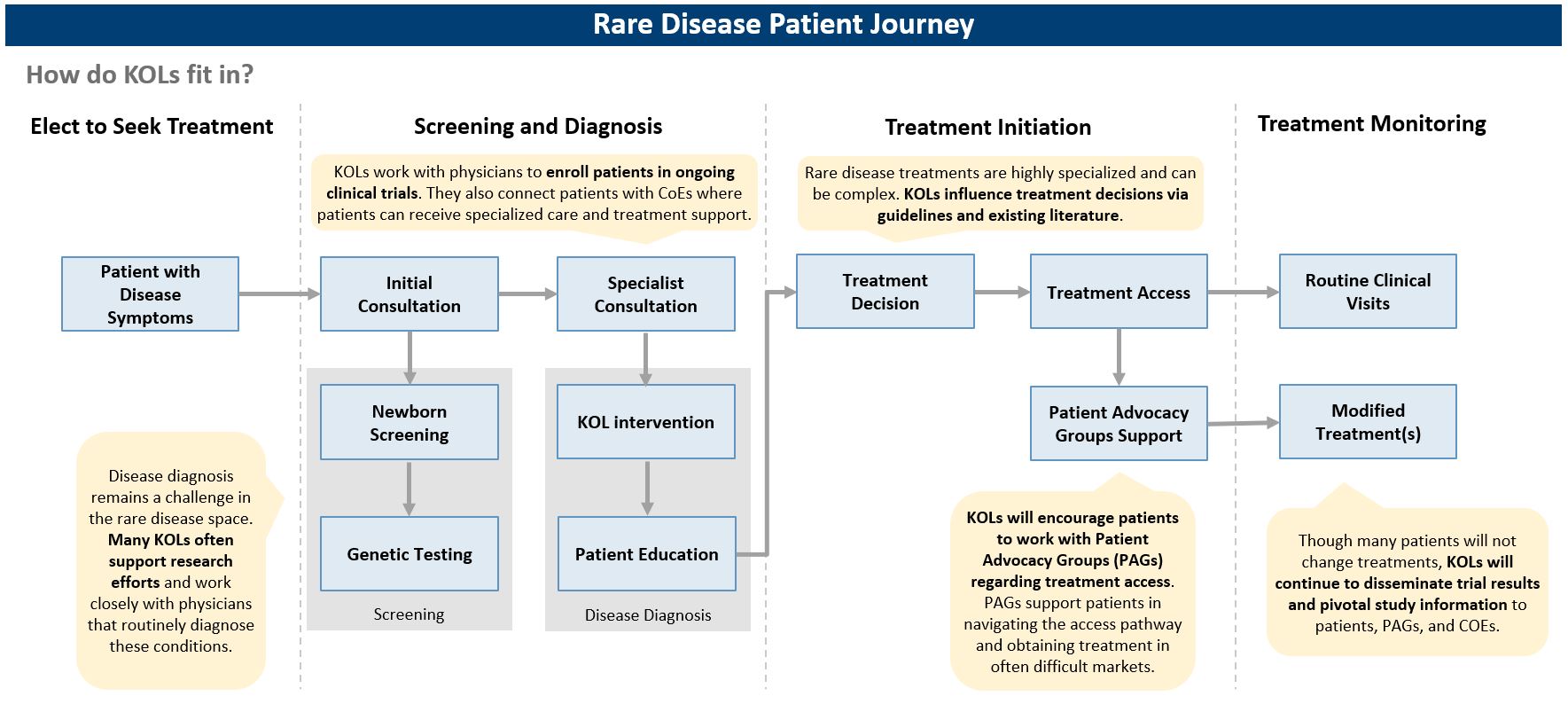
The first step in entering a market is to identify which markets offer a path to reimbursement with sufficient pricing potential. The next step is assessing your pricing flexibility, as offering a lower price than in the US or even the EU5 can increase the likelihood of reimbursement in key OUS markets. When making these assessments, identifying patient access schemes, such as named patient supply (NPS), can validate and drive demand. Once an orphan drug gains regulatory approval, companies must be prepared to work with stakeholders, such as patient advocacy groups and KOLs, to demonstrate need for the orphan drug, clinical and cost effectiveness, and drive favorable reimbursement decisions. These stakeholders are pivotal in some markets, ensuring that patients can get treatments at affordable costs throughout the duration of their treatment. As an example, in Brazil, patient advocacy groups work closely with patients to navigate court systems that enable patients to make a legislative case for drug access and coverage before national approval, including for orphan drugs (see more below).
External Reference Pricing
External reference pricing adds significant complexity to global market access strategy as the application of referencing varies greatly among countries, including:
- Product Applicability: categories of products for which referencing is applied, including referencing only for drugs in a specific care setting (e.g., inpatient hospital), innovative medicines for which there is no alternative available on the market, or high-cost medicines
- Basket Composition: both the total number and specific countries selected to include in the reference basket (typically selected based on comparable GDP per capita)
- Calculation Method: use of either an average price or selection of the lowest price of basket countries
- Decision Process: whether used as the main systematic criterion (most common) or as supportive information only when setting a drug price
- Re-evaluation: pricing must be re-evaluated frequently after initial price is set
In Europe, the vast majority of countries use some form of reference pricing. With reference pricing, there is increased pricing interdependence between countries. Given the high prices of orphan drugs, it is critical for rare disease companies to develop a launch sequencing strategy that factors in price referencing. This could include strategically launching first in high-priced countries without reference pricing, then focusing on lower-priced countries.
Real-World Evidence
RWE is gaining momentum globally as real-world data (RWD) sources become available—specifically electronic health records and claims data that provide a basis for evaluating outcomes. New treatment costs remain high for rare diseases, putting pressure on pharma and biotech companies to demonstrate results for premium pricing with payers. Gene therapies are especially costly due to their complexity, making RWE an ideal tool. A prime example is the AveXis-Novartis approach to payer contracting with Zolgensma, a one-time gene therapy treatment that replaces lifetime chronic therapy for patients with spinal muscular atrophy Type 1, and which launched in the US in June 2019. Gene therapies are breaking pricing norms since manufacturers are only able to generate revenue from “one-shot” treatment for each patient, and Zolgensma made waves with a US price point of $2.1M per patient—the most expensive treatment on the market as of this writing. Novartis worked with payers to establish efficacy-based reimbursement and a 5-year installment payment option to spread payment for treatment over time. With these arrangements, risk is lower for payers, who can pay $425K annually for five years and better justify a patient switch from Biogen’s Spinraza, a chronic treatment estimated to cost $4M+ over a 10-year period. Zolgensma won coverage for 90% of US commercial patients within its first full quarter on the market, with all payers taking advantage of value-based contracting; however, initial uptake of the installment-based payment system was limited.
Similarly, in May of this year, Zolgensma received conditional approval in Europe with the “Day One” access program, which ensures the cost of patients treated before national pricing and reimbursement agreements are in place aligns with the value-based prices negotiated following clinical and economic assessments. Working within the existing pricing and local reimbursement frameworks, the “Day One” access program for EU governments and reimbursement agencies allows the company to tackle entry into markets faster and with more flexibility. This system sets up a win for each stakeholder: the patient, the health and reimbursement bodies, and AveXis-Novartis. With the Temporary Authorization for Use (ATU) program, it became immediately accessible in France and should be available in Germany shortly.
Coverage for therapies like Zolgensma remains dependent on demonstrating values, so companies must leverage proof of value when looking to capture new patient markets. RWE and patient-reported outcomes (PROs) provide stakeholders with concrete data to inform formulary addition and clinical trial outcome endpoints.
Moving Forward
An effective global market access strategy for orphan drugs must be adaptable to different regions and their unique challenges to be effective. As companies work through the key questions outlined above to create a successful global market access strategy, tools like RWE and external reference pricing can support tackling a large range of location-specific issues.
How Kx Can Help
Our experts evaluate business opportunities, deliver top-notch expertise, and make data-driven recommendations to our healthcare clients. Kx Advisors can guide your organization through the process of developing and implementing a global market access strategy for your rare disease drug.
Sources
https://www.pacificbridgemedical.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/03/Orphan-Drugs-in-Asia-2017.pdf
http://info.evaluategroup.com/rs/evaluatepharmaltd/images/2014OD.pdf
https://www.europeanpharmaceuticalreview.com/article/62846/orphan-drugs-regulation-eu/
https://ec.europa.eu/health/sites/health/files/files/committee/stamp/2015-05_stamp2/5.pdf
https://www.eurordis.org/training-health-technology-assessment
https://www.rtihs.org/sites/default/files/Rare%20Disease%20Webinar%20Slides_Final%20Feb%2027.pdf
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4802694/
https://mapbiopharma.com/home/2020/04/landmark-pay-for-performance-contract-agreed-in-germany/